Onscreen text/quote bubbles:
Improvement Over Time: An Update on Charlene 2+ Years Later
Age: 65
Primary condition: Schizoaffective disorder
Disclaimer at bottom of screen:
This was an individual patient’s experience on AUSTEDO BID. Results may vary.
Onscreen text/quote bubbles:
“After a little over two years on AUSTEDO…my feet aren’t moving all the time. My hands aren’t moving all the time.”
“I can do something else with my hands now. I can tie my shoes…I can do things that people consider normal, that weren’t normal for me.”
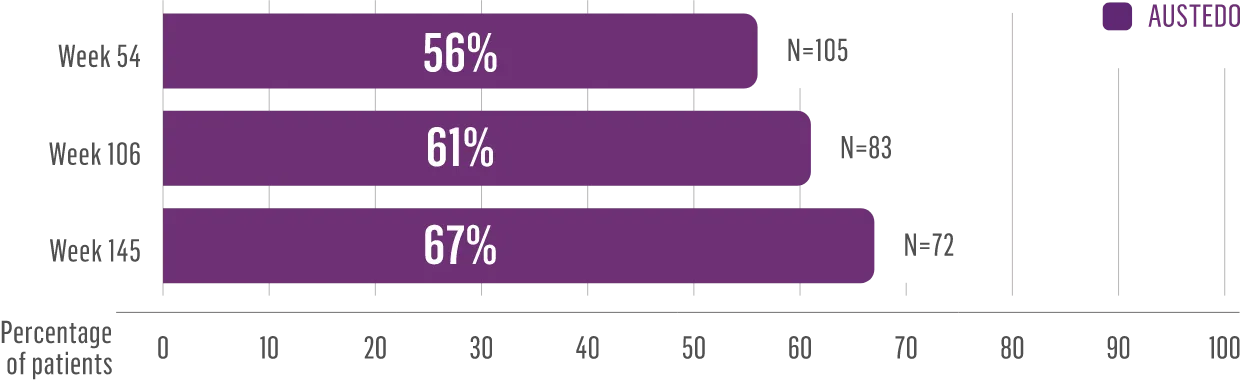
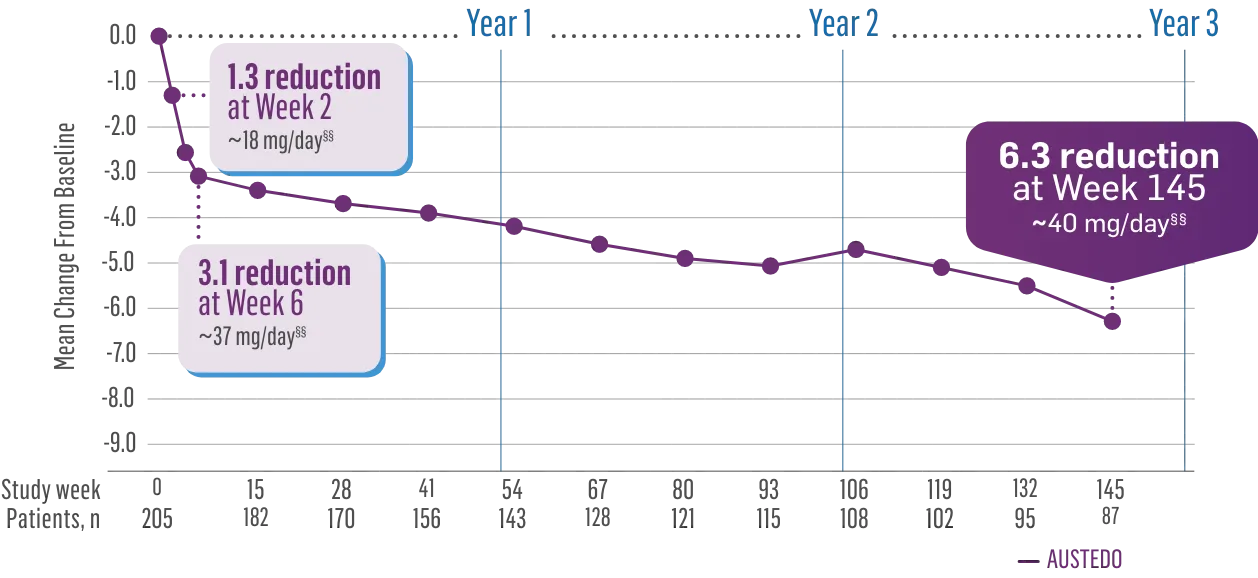
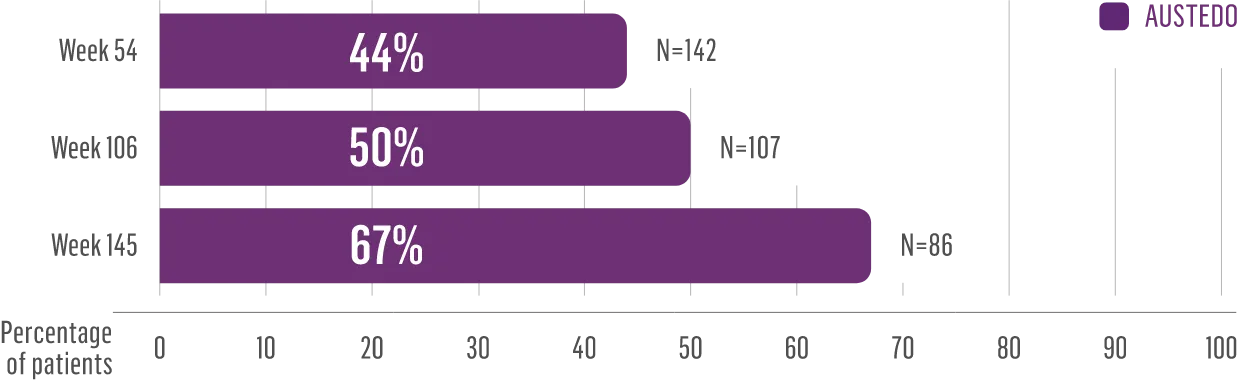
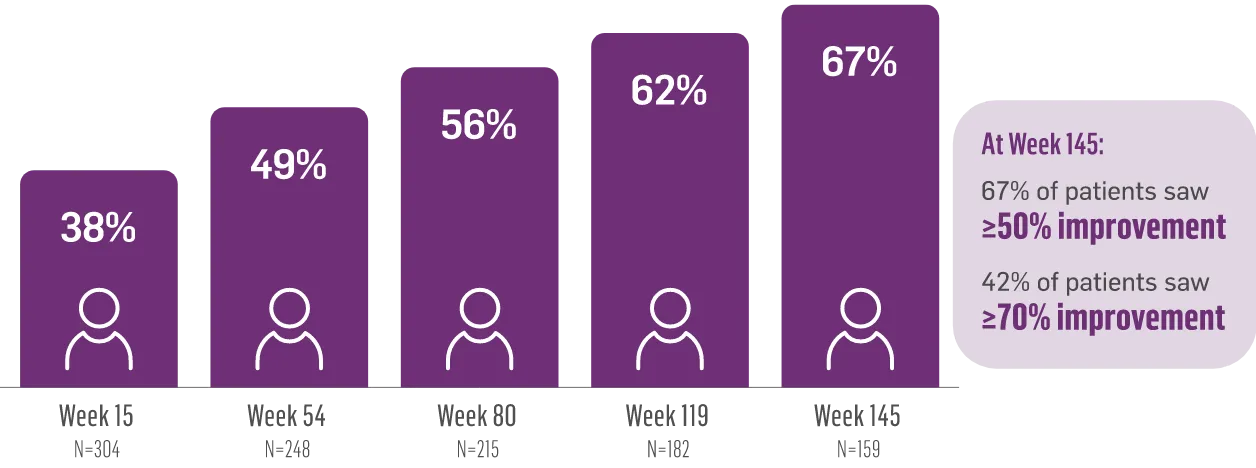
CHARLENE’S JOURNEY OVER 2+ YEARS
When Charlene developed TD, she was told her involuntary movements would last forever. But she wasn’t ready to give up…
After starting AUSTEDO, Charlene began to see an improvement in her involuntary movements.
“I used to move my fingers without realizing, and I rocked…and I’m not doing that hardly at all…it is better.” – Charlene
“So do you think we’re at the right dose…or do you think we still have room for improvement?” – HCP
“I think there’s room for improvement.” – Charlene
As her dose was increased, Charlene’s movements continued to improve.
“Your movements look better…your fingers look pretty stable…” – HCP
“Yeah, and my mouth isn’t going 20 miles per hour…” – Charlene
Charlene’s doctor increased her dose to 48 mg/day, where Charlene experienced effective and tolerable symptom improvement.
Now, more than 2 years after starting treatment, Charlene can’t imagine going back to life without AUSTEDO.
“After a little over two years on AUSTEDO…my feet aren’t moving all the time. My hands aren’t moving all the time.” – Charlene
“I can do something else with my hands now. I can tie my shoes…I can do things that people consider normal, that weren’t normal for me.” – Charlene
“I don’t want to go back to the motions, so I prefer to stay on AUSTEDO…it helps and I don’t want to lose that.” – Charlene
Disclaimer at bottom of screen:
No clinical trials have been conducted to suggest that AUSTEDO affects the outcomes listed above.
Onscreen text/quote bubbles:
What could long-term results mean for your patients like Charlene?
See the rest of Charlene’s story at AUSTEDOhcp.com
Disclaimer at bottom of screen:
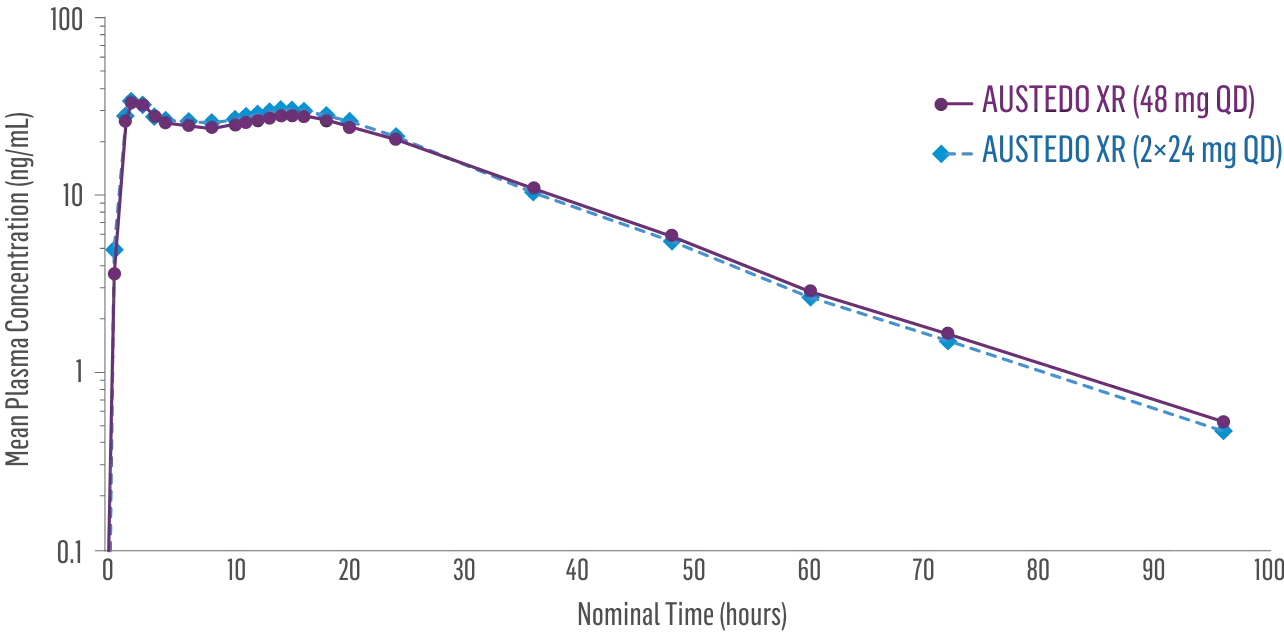
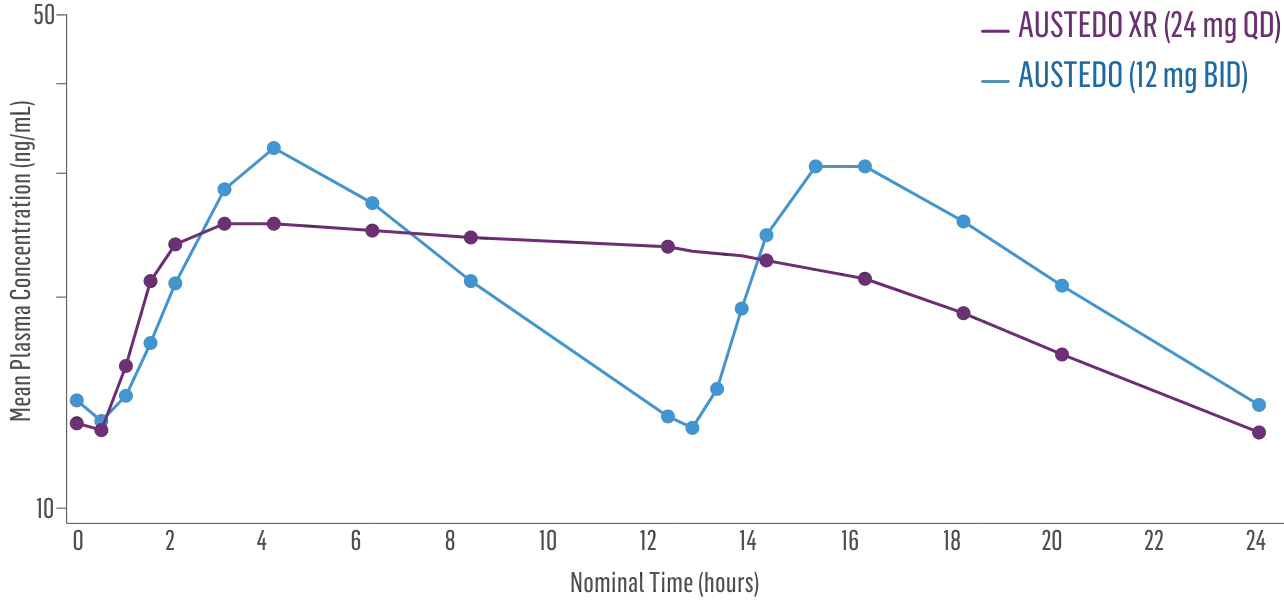
Once-daily AUSTEDO XR Is available.
Bioequivalence of once-daily AUSTEDO XR has been established with AUSTEDO BID based on pharmacokinetic profile studies. When two formulations are shown to be bioequivalent, they are considered to be therapeutically equivalent.
Onscreen ISI scroll:
INDICATIONS AND USAGE AUSTEDO XR (deutetrabenazine) extended-release tablets and AUSTEDO (deutetrabenazine) tablets are indicated in adults for the treatment of chorea associated with Huntington’s disease and for the treatment of tardive dyskinesia.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Depression and Suicidality in Patients with Huntington’s Disease:
AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO can increase the risk of depression and suicidal thoughts and behavior (suicidality) in patients with Huntington’s disease. Balance the risks of depression and suicidality with the clinical need for treatment of chorea. Closely monitor patients for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidality, or unusual changes in behavior. Inform patients, their caregivers, and families of the risk of depression and suicidality and instruct them to report behaviors of concern promptly to the treating physician. Exercise caution when treating patients with a history of depression or prior suicide attempts or ideation. AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are contraindicated in patients who are suicidal, and in patients with untreated or inadequately treated depression.
Contraindications: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are contraindicated in patients with Huntington’s disease who are suicidal, or have untreated or inadequately treated depression. AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are also contraindicated in: patients with hepatic impairment; patients taking reserpine or within 20 days of discontinuing reserpine; patients taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), or within 14 days of discontinuing MAOI therapy; and patients taking tetrabenazine or valbenazine.
Clinical Worsening and Adverse Events in Patients with Huntington’s Disease: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may cause a worsening in mood, cognition, rigidity, and functional capacity. Prescribers should periodically re-evaluate the need for AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO in their patients by assessing the effect on chorea and possible adverse effects.
QTc Prolongation: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may prolong the QT interval, but the degree of QT prolongation is not clinically significant when AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO is administered within the recommended dosage range. AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO should be avoided in patients with congenital long QT syndrome and in patients with a history of cardiac arrhythmias.
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS), a potentially fatal symptom complex reported in association with drugs that reduce dopaminergic transmission, has been observed in patients receiving tetrabenazine. The risk may be increased by concomitant use of dopamine antagonists or antipsychotics. The management of NMS should include immediate discontinuation of AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO; intensive symptomatic treatment and medical monitoring; and treatment of any concomitant serious medical problems.
Akathisia, Agitation, and Restlessness: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may increase the risk of akathisia, agitation, and restlessness. The risk of akathisia may be increased by concomitant use of dopamine antagonists or antipsychotics. If a patient develops akathisia, the AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO dose should be reduced; some patients may require discontinuation of therapy.
Parkinsonism: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may cause parkinsonism in patients with Huntington’s disease or tardive dyskinesia. Parkinsonism has also been observed with other VMAT2 inhibitors. The risk of parkinsonism may be increased by concomitant use of dopamine antagonists or antipsychotics. If a patient develops parkinsonism, the AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO dose should be reduced; some patients may require discontinuation of therapy.
Sedation and Somnolence: Sedation is a common dose-limiting adverse reaction of AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO. Patients should not perform activities requiring mental alertness, such as operating a motor vehicle or hazardous machinery, until they are on a maintenance dose of AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO and know how the drug affects them. Concomitant use of alcohol or other sedating drugs may have additive effects and worsen sedation and somnolence.
Hyperprolactinemia: Tetrabenazine elevates serum prolactin concentrations in humans. If there is a clinical suspicion of symptomatic hyperprolactinemia, appropriate laboratory testing should be done and consideration should be given to discontinuation of AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO.
Binding to Melanin-Containing Tissues: Deutetrabenazine or its metabolites bind to melanin-containing tissues and could accumulate in these tissues over time. Prescribers should be aware of the possibility of long-term ophthalmologic effects.
Common Adverse Reactions: The most common adverse reactions for AUSTEDO (>8% and greater than placebo) in a controlled clinical study in patients with Huntington’s disease were somnolence, diarrhea, dry mouth, and fatigue. The most common adverse reactions for AUSTEDO (4% and greater than placebo) in controlled clinical studies in patients with tardive dyskinesia were nasopharyngitis and insomnia. Adverse reactions with AUSTEDO XR extended-release tablets are expected to be similar to AUSTEDO tablets. Please see full Prescribing Information, including Boxed Warning, on AUSTEDOhcp.com.
Onscreen text:
This was an individual patient’s experience. Results may vary.
REFERENCES: AUSTEDO XR® (deutetrabenazine) extended-release tablets and AUSTEDO® current Prescribing Information. Parsippany, NJ: Teva Neuroscience, Inc. Chow SC. Bioavailability and bioequivalence in drug development. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Comput Stat. 2014;6(4):304-312. Data on file. Parsippany, NJ: Teva Neuroscience, Inc.