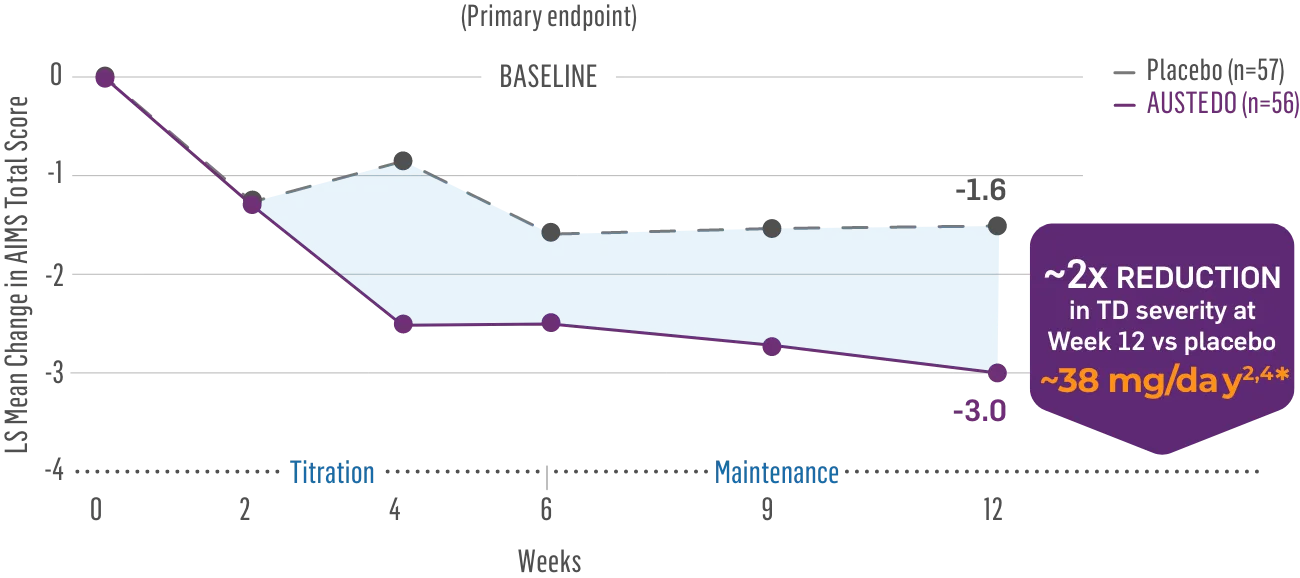
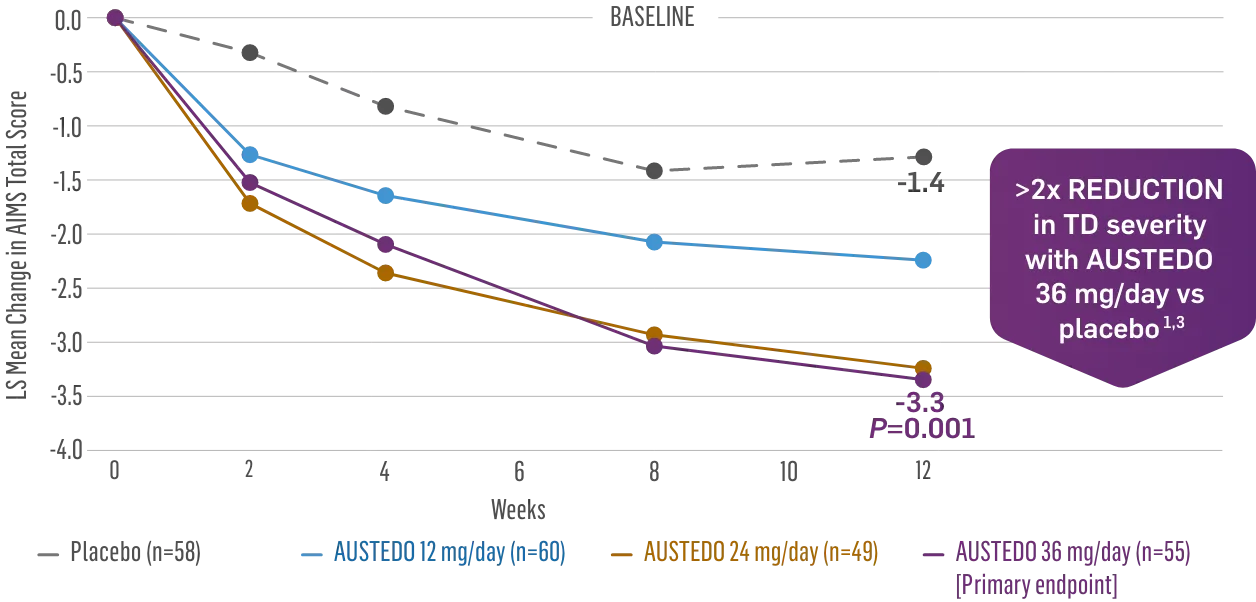
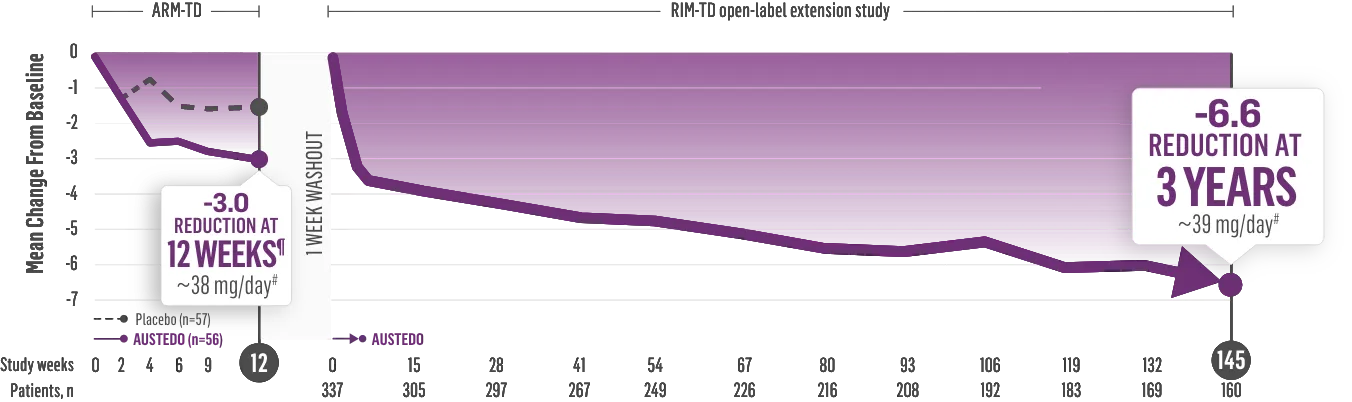
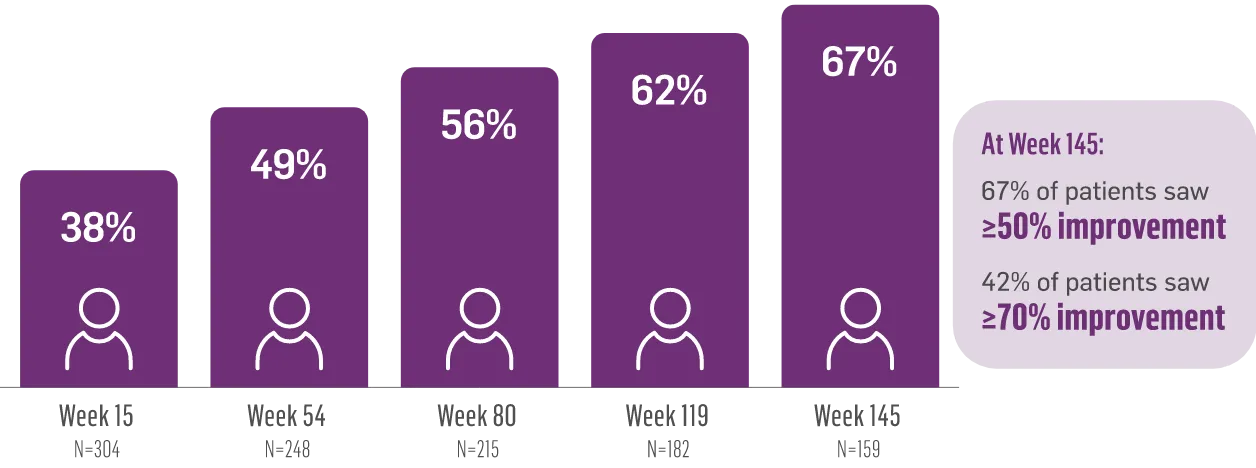
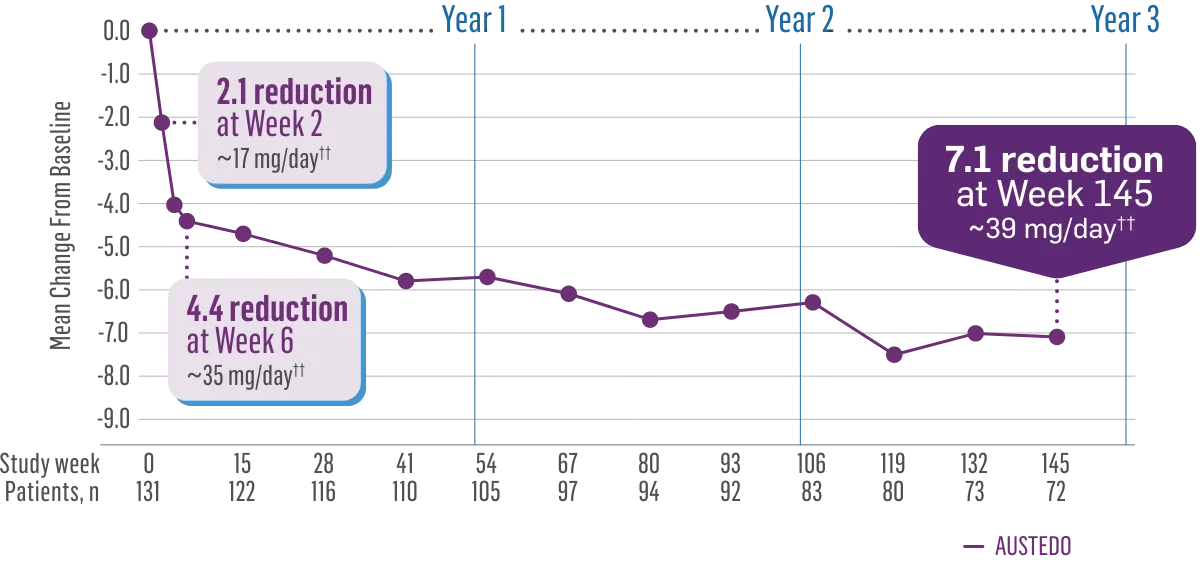
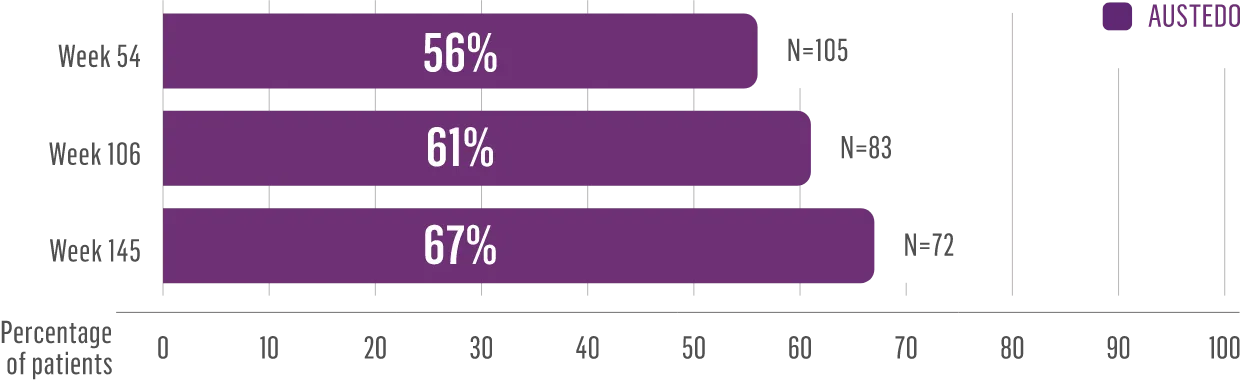
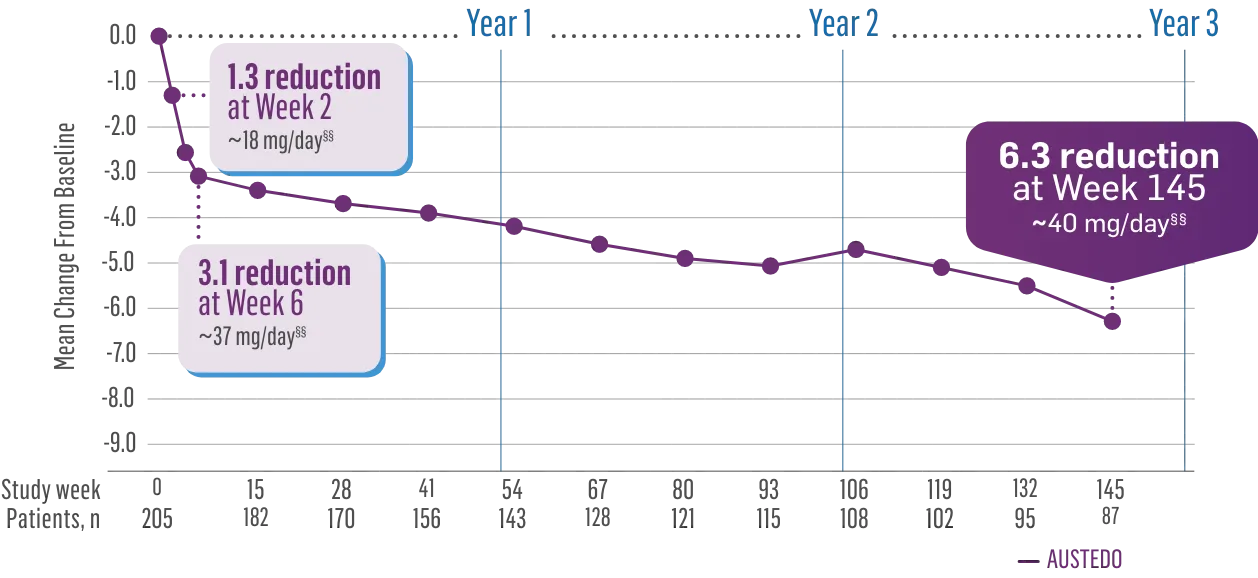
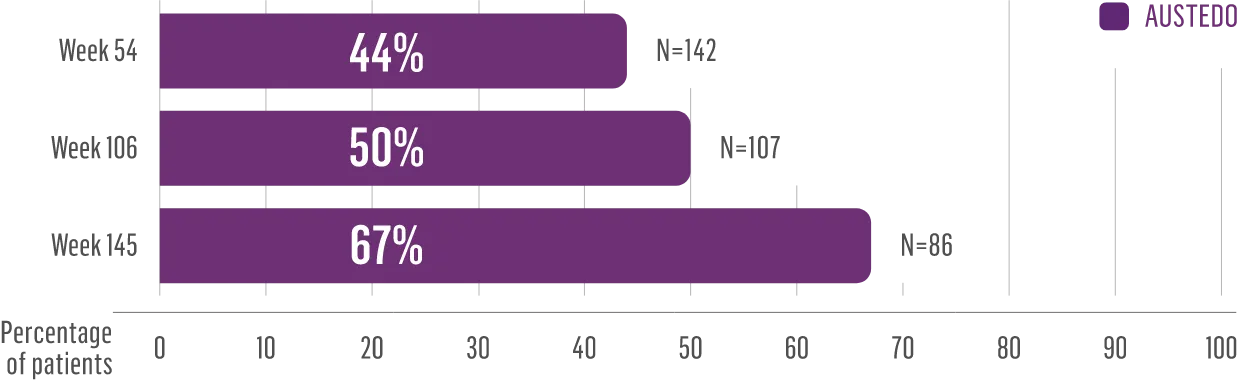
The largest elderly population of any TD clinical study (n=78)
Sustained results across 3 years for elderly patients (aged ≥65 years) and younger patients (aged 21-64 years)††
Elderly and Younger Subgroups: AIMS Score Reduction in RIM-TD
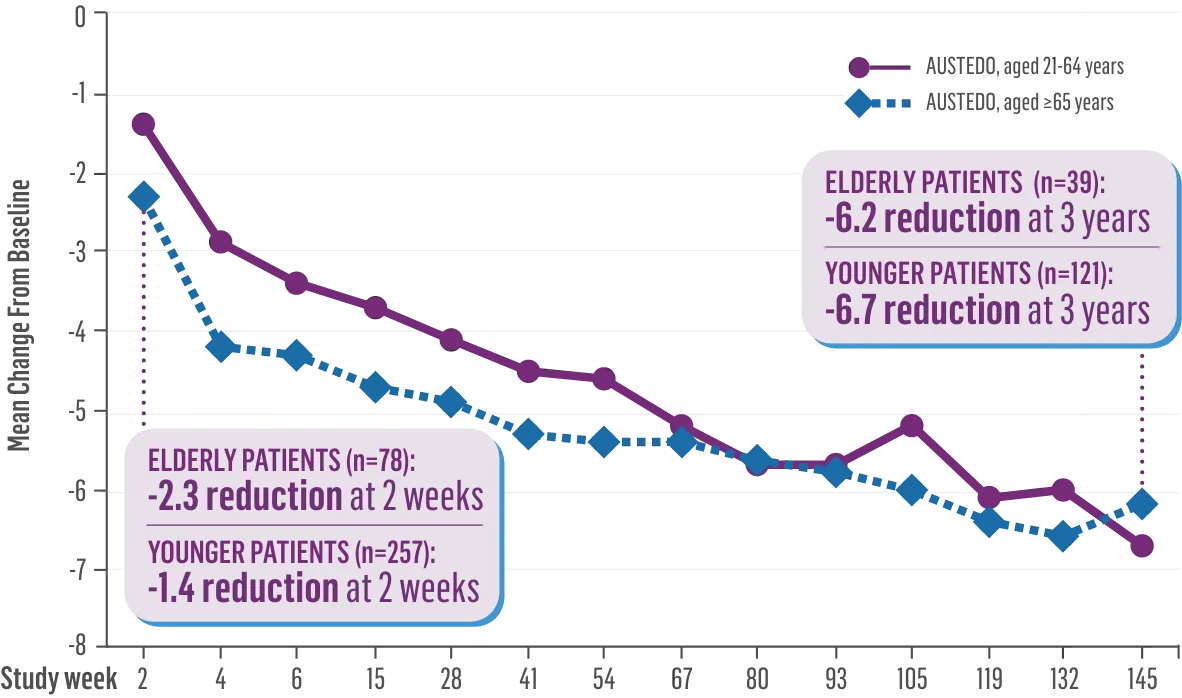
Similar dose and response at Week 145 (>36 mg/day)‡‡
Similar safety and tolerability profile
Similar percentage of patients remained in the study at Week 145
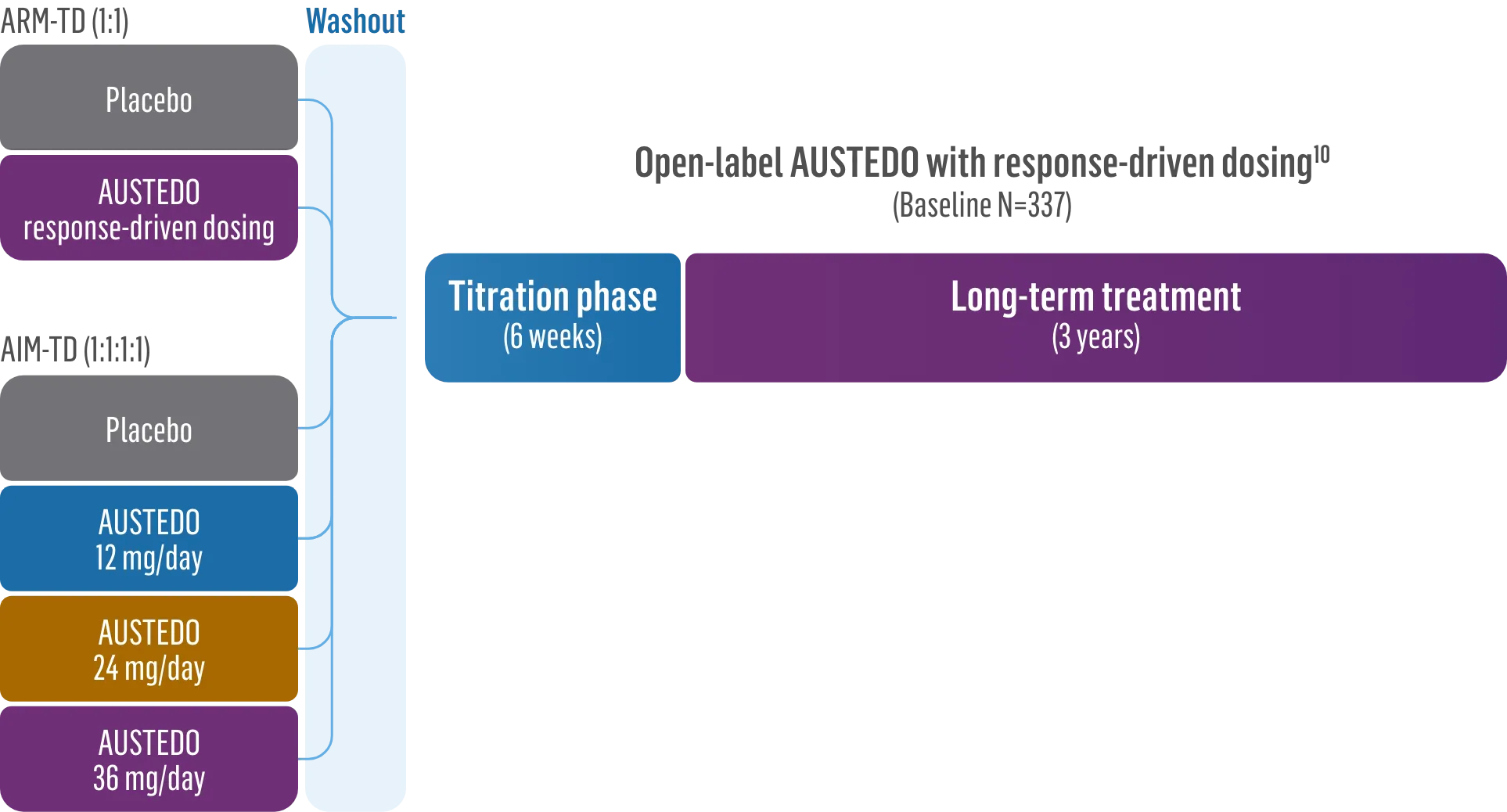
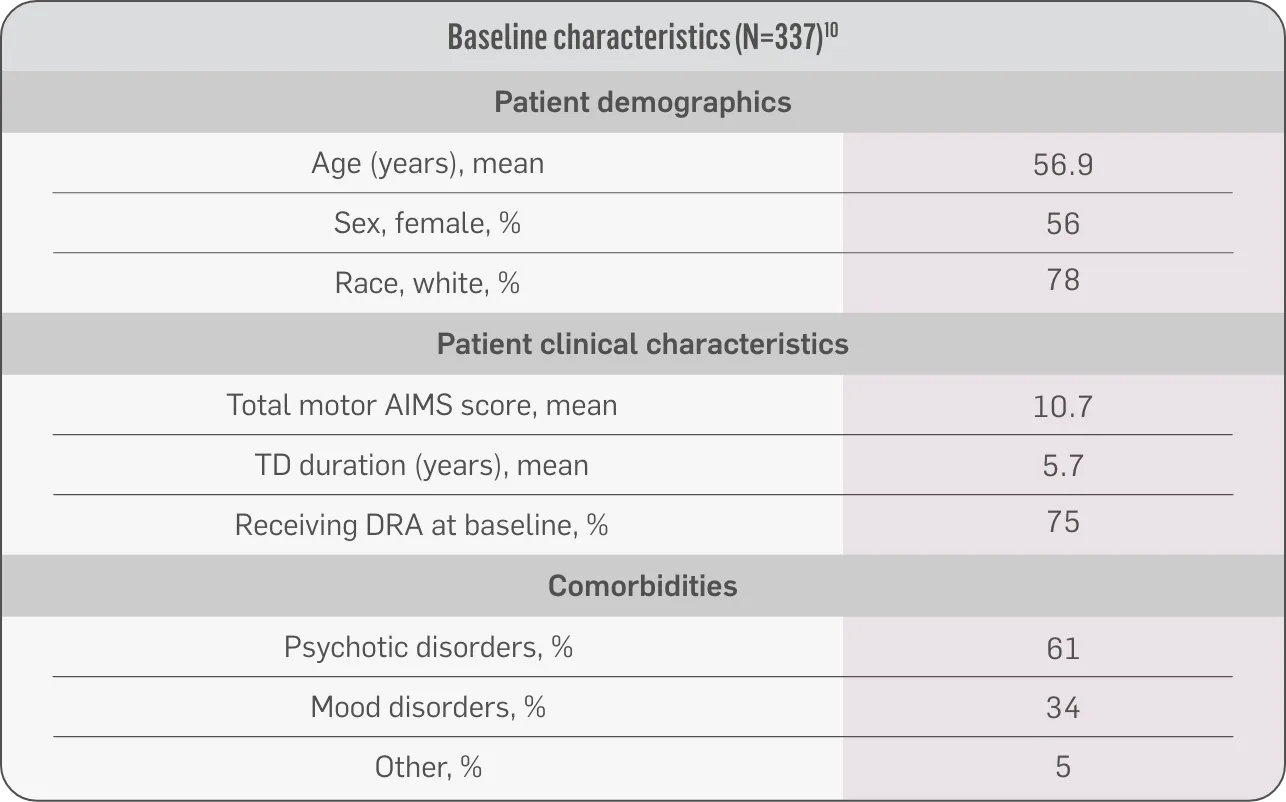
Patients in the RIM-TD study received the AUSTEDO BID formulation.1,5
See a long-term care resident’s journey with TD movement improvement

Onscreen text:
TREATING TD IN LTC
NORMA’S SYMPTOM IMPROVEMENT STORY
Age:79
Primary conditions: Mood disorder, anxiety disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and primary insomnia, along with pulmonary, cardiovascular, and gastrointestinal issues
Disclaimer on bottom of screen:
This was an individual patient’s experience. Results may vary. Participants were compensated by Teva Neuroscience, Inc.
LTC, long-term care; TD, tardive dyskinesia.
Onscreen text:
Norma is an LTC resident with TD. Before treatment, she had a moderate Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale (AIMS) score of 7.
Her involuntary movements were significantly impacting her physical, psychological, and social health.
Dr. Patel:
I was given consultation on Norma initially for treatment of her psychiatric condition. And the first time I saw her is when I noticed she had symptoms of tardive dyskinesia.
Her ability to swallow was affected. She had trouble with a lot of drooling because of her tardive dyskinesia and tongue movements and jaw movements. So she constantly had to carry a washcloth and wipe her mouth all the time, and she was embarrassed by it. She was always scared that she would choke.
Onscreen text:
DR. AMITA PATEL, MD
GERIATRIC PSYCHIATRIST IN LTC
Dr. Patel:
Norma’s tardive dyskinesia movements were severe enough that it really destabilized her underlying mental health condition, and I had to adjust her psychoactive medications for it.
Onscreen text:
KIM MIDDLETON
DIRECTOR OF NURSING IN LTC
Kim:
I think the movements affected Norma physically. Functionally, she needed more help with her ADLs or her activities of daily living, such as getting dressed, toileting, even just brushing her teeth—just the everyday functions of her life.
Onscreen text:
JENNIFER
NORMA’S DAUGHTER
Jennifer:
I talk to my mom a lot, and when I can't understand her, you know, that's hard for me. It's definitely hard for her because I have to have her repeat things all the time.”
The physical activities changed. She kind of had to stop, you know, crocheting and certain things like that.
Onscreen text:
Any resident who has taken or is currently taking an antipsychotic is at risk for developing TD.
Fortunately, Norma’s care team recognized her TD symptoms and the negative impact they were having on her life.
Dr. Patel:
The symptoms that we saw in Norma are not only typical for Norma, we see that quite often in other residents that I treat with tardive dyskinesia in long-term care facility. Just because residents are in long-term care facility, doesn't mean they don't deserve maximum quality of life.
Treating TD was really important for Norma because TD was not only affecting her socially, physically, and psychologically, but it was worsening her depression and anxiety.
It was very important for me to pick the correct medication, where there is no drug interaction with the current regimen she's on because she was quite stable on her current mental health medication, and I didn't want to adjust any of her current psychoactive medication, if possible.
Onscreen Indication and Black Box Warning:
AUSTEDO XR® and AUSTEDO® are indicated in adults for the treatment of tardive dyskinesia and for the treatment of chorea associated with Huntington's disease.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Depression and Suicidality in Patients with Huntington’s Disease: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO can increase the risk of depression and suicidal thoughts and behavior (suicidality) in patients with Huntington’s disease. Balance the risks of depression and suicidality with the clinical need for treatment of chorea. Closely monitor patients for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidality, or unusual changes in behavior. Inform patients, their caregivers, and families of the risk of depression and suicidality and instruct them to report behaviors of concern promptly to the treating physician. Exercise caution when treating patients with a history of depression or prior suicide attempts or ideation. AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are contraindicated in patients who are suicidal, and in patients with untreated or inadequately treated depression.
Please see additional Important Safety Information at the end of this video.
Dr. Patel:
I have had a lot of experience using AUSTEDO XR in other patients. I've had great results with this medication, especially in Norma’s case.
It was easy to add AUSTEDO XR to the current medications that Norma was taking. I could do a slow titration and watch for any side effects.
Onscreen text:
Once Norma began treatment, she saw a significant improvement in her movements—and so did those around her.
Onscreen text:
Before treatment AIMS score of 7
After treatment AIMS score of 3
Dr. Patel:
Norma is currently on 48 milligrams and her current AIMS score is 3. But if you really talk about the improvement she has had, it really has given her better quality of life. She is now able to speak better. We don't have to ask her to repeat herself all the time. She doesn't have to carry the washcloth to wipe her lips all the time. She is not afraid of choking. Her movements of her jaw and her fingers are so much better. She's not embarrassed. She's not afraid that people are going to make fun of her.
Kim:
I could tell that AUSTEDO XR was making a difference in Norma's life.
I noticed that she was being involved more in the social activities due to the involuntary movements decreasing. So, I feel like Norma's quality of life was improving.
I think her movement improvement has made it easier to care for her because she is more independent. She can do more of those, you know, daily things on her own.
Jennifer:
My feeling since she started taking AUSTEDO XR, is relief. I don't have to worry quite as much about her possibly hurting herself or even with eating or drinking and choking. And I feel I'm proud of her for her leaps and bounds.
It has been a very noticeable change. As time goes by, she can do a little bit more and a little bit more. And when she handed me that little blanket that she made, I was really shocked because the stitching was really great.
When I see Mom's progress, it just fills me with joy. It's a relief to know that she is getting the help, the care, and the medications that she needs.
Kim:
So it's important to identify TD symptoms and to help people we identify with those movements to get them treatment, to decrease the risk of them falling, or having to go to the emergency department, or losing weight.
I think the care team, I can probably speak for all of them. When you see someone like Norma improve their quality of life, I think I can say that it just brings a lot of joy to our hearts and our lives. And it just reaffirms why we come here every day and why we do what we do.
Onscreen text:
Learn more about AUSTEDO XR and how it can make a difference for your residents with TD.
Onscreen ISI scroll:
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are indicated in adults for the treatment of tardive dyskinesia and for the treatment of chorea associated with Huntington's disease.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Depression and Suicidality in Patients with Huntington’s Disease: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO can increase the risk of depression and suicidal thoughts and behavior (suicidality) in patients with Huntington’s disease. Balance the risks of depression and suicidality with the clinical need for treatment of chorea. Closely monitor patients for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidality, or unusual changes in behavior. Inform patients, their caregivers, and families of the risk of depression and suicidality and instruct them to report behaviors of concern promptly to the treating physician. Exercise caution when treating patients with a history of depression or prior suicide attempts or ideation. AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are contraindicated in patients who are suicidal, and in patients with untreated or inadequately treated depression.
Contraindications: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are contraindicated in patients with Huntington’s disease who are suicidal, or have untreated or inadequately treated depression. AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are also contraindicated in: patients with hepatic impairment; patients taking reserpine or within 20 days of discontinuing reserpine; patients taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), or within 14 days of discontinuing MAOI therapy; and patients taking tetrabenazine or valbenazine.
Clinical Worsening and Adverse Events in Patients with Huntington’s Disease: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may cause a worsening in mood, cognition, rigidity, and functional capacity. Prescribers should periodically re-evaluate the need for AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO in their patients by assessing the effect on chorea and possible adverse effects.
QTc Prolongation: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may prolong the QT interval, but the degree of QT prolongation is not clinically significant when AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO is administered within the recommended dosage range. AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO should be avoided in patients with congenital long QT syndrome and in patients with a history of cardiac arrhythmias.
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS), a potentially fatal symptom complex reported in association with drugs that reduce dopaminergic transmission, has been observed in patients receiving tetrabenazine. The risk may be increased by concomitant use of dopamine antagonists or antipsychotics. The management of NMS should include immediate discontinuation of AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO; intensive symptomatic treatment and medical monitoring; and treatment of any concomitant serious medical problems.
Akathisia, Agitation, and Restlessness: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may increase the risk of akathisia, agitation, and restlessness. The risk of akathisia may be increased by concomitant use of dopamine antagonists or antipsychotics. If a patient develops akathisia, the AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO dose should be reduced; some patients may require discontinuation of therapy.
Parkinsonism: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may cause parkinsonism in patients with Huntington’s disease or tardive dyskinesia. Parkinsonism has also been observed with other VMAT2 inhibitors. The risk of parkinsonism may be increased by concomitant use of dopamine antagonists or antipsychotics. If a patient develops parkinsonism, the AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO dose should be reduced; some patients may require discontinuation of therapy.
Sedation and Somnolence: Sedation is a common dose-limiting adverse reaction of AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO. Patients should not perform activities requiring mental alertness, such as operating a motor vehicle or hazardous machinery, until they are on a maintenance dose of AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO and know how the drug affects them. Concomitant use of alcohol or other sedating drugs may have additive effects and worsen sedation and somnolence.
Hyperprolactinemia: Tetrabenazine elevates serum prolactin concentrations in humans. If there is a clinical suspicion of symptomatic hyperprolactinemia, appropriate laboratory testing should be done and consideration should be given to discontinuation of AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO.
Binding to Melanin-Containing Tissues: Deutetrabenazine or its metabolites bind to melanin-containing tissues and could accumulate in these tissues over time. Prescribers should be aware of the possibility of long-term ophthalmologic effects.
Common Adverse Reactions: The most common adverse reactions for AUSTEDO (>8% and greater than placebo) in a controlled clinical study in patients with Huntington’s disease were somnolence, diarrhea, dry mouth, and fatigue. The most common adverse reactions for AUSTEDO (4% and greater than placebo) in controlled clinical studies in patients with tardive dyskinesia were nasopharyngitis and insomnia. Adverse reactions with AUSTEDO XR extended-release tablets are expected to be similar to AUSTEDO tablets.
Please see full Prescribing Information, including Boxed Warning, at AUSTEDOhcp.com.
††In a post hoc subgroup analysis of RIM-TD.
‡‡Mean total dose.