3 years of sustained chorea improvement and tolerability data1‑3
ARC-HD Study: TMC Score Reduction Maintained Through 3 Years4
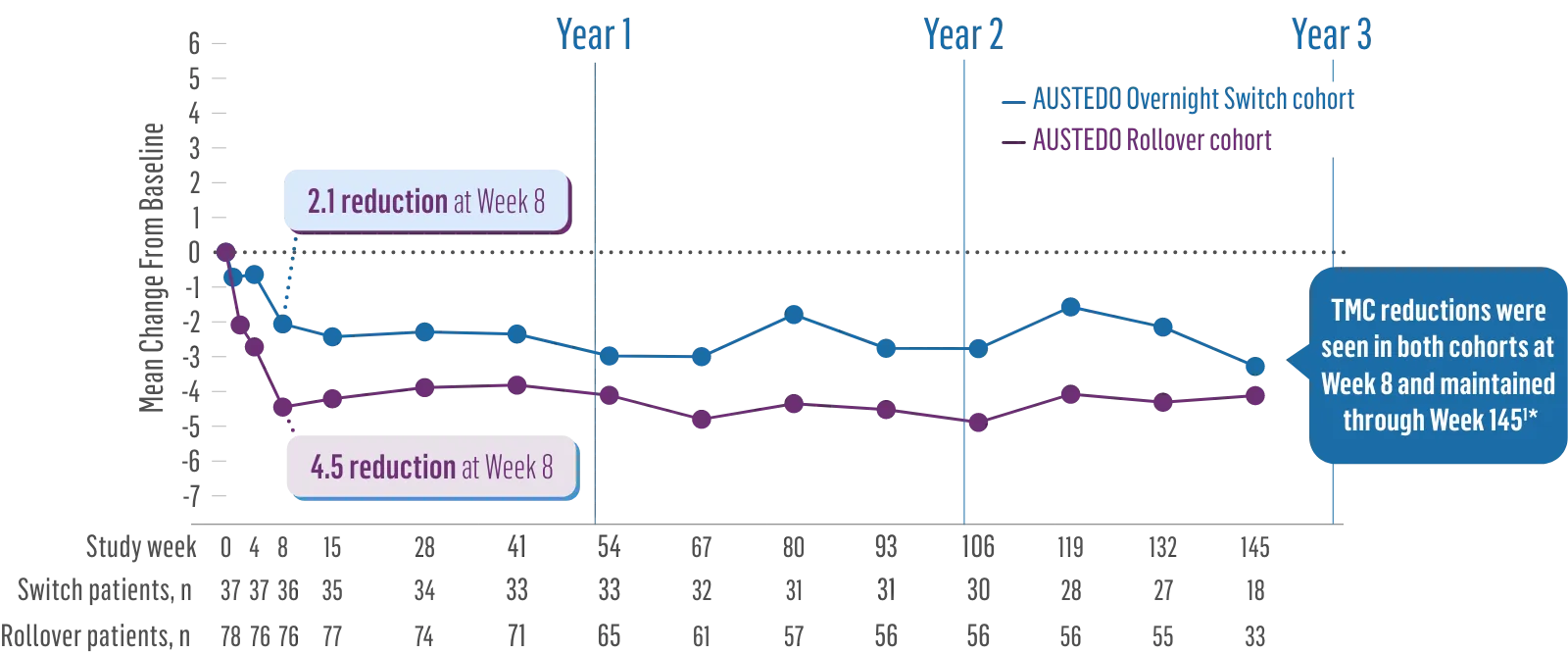
TMC reductions were seen in both cohorts at Week 8 and maintained through Week 1451*
Patients in the ARC-HD study received the AUSTEDO BID formulation.1,5
No new safety concerns over 3 years compared to pivotal study1
Learn more about the ARC-HD study
*ARC-HD was divided into 2 study cohorts: patients who rolled over from the pivotal trial and patients who switched overnight from tetrabenazine.1
Sustained concentrations with a single daily pill
- Bioequivalence established between single-pill and multiple-pill doses of once-daily AUSTEDO XR based on pharmacokinetic studies4,5
- Data support bioequivalence of single-pill and multiple-pill AUSTEDO XR across full dosing range5
Plasma Concentration Over 96 Hours: AUSTEDO XR 48 mg vs AUSTEDO XR 2×24 mg QD4†
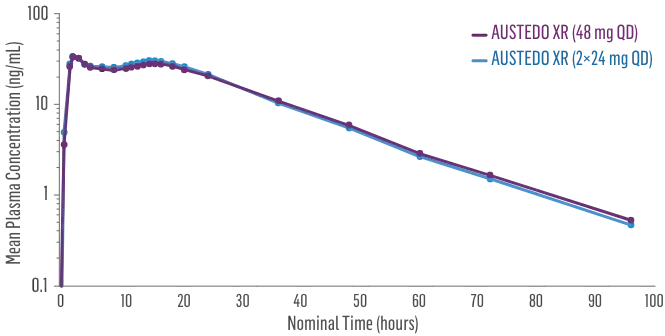
†Based on active alpha and beta metabolites.4
- Bioequivalence of once-daily AUSTEDO XR has been established in pharmacokinetic profile studies4‡
- Peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) of AUSTEDO® XR (deutetrabenazine) extended-release tablets are reached within approximately 3 hours5
Plasma Concentration at Steady State Over 24 Hours: AUSTEDO XR vs BID4§
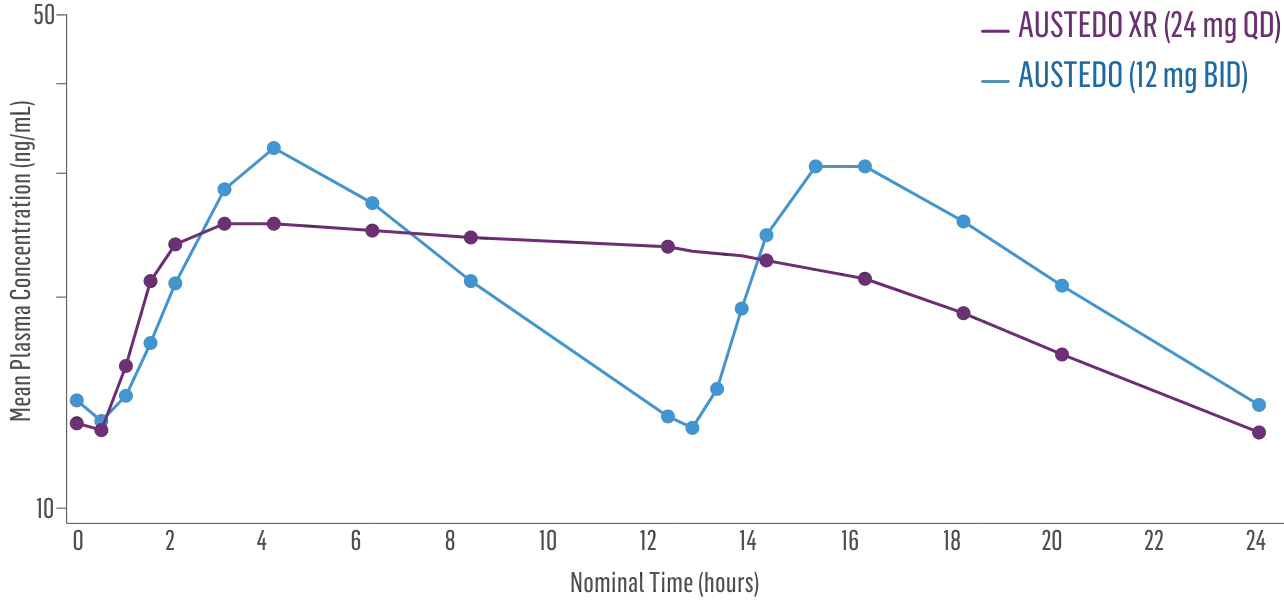
‡Data support bioequivalence of XR and BID across the full dosing range of AUSTEDO.5
§Based on active alpha and beta metabolites.4
TMS, total motor score; UHDRS, Unified Huntington’s Disease Rating Scale.
See what long-term results mean for real patients
Watch: A Real Patient’s Experience
Ray and Rhonda’s long-term journey with HD chorea.
Ray:
I’m Ray…I’m 55.
Rhonda:
My name is Rhonda, and I am Ray’s wife.
Disclaimer at bottom of screen:
This was an actual patient’s experience. Results may vary. Ray and Rhonda were compensated for their participation in this video.
Onscreen text:
Ray and Rhonda were looking forward to spending their retirement hiking, traveling, and enjoying their grandchildren.
But when Ray was diagnosed with HD in 2019, it seemed like chorea would make all of that impossible.
Rhonda:
Ray’s dad had Huntington’s disease…he wasn’t able to walk…he ended up in a wheelchair…
So that was kind of a really scary thought for me. I just assumed that our lives…would be over very soon as we knew it…
Onscreen text:
As Ray’s disease progressed, his chorea began to affect him day and night.
Rhonda:
So the first symptoms I noticed of his chorea was at night while he was sleeping. His arms would, you know, kind of start flailing and hitting and then kind of it would just be like his whole body…
Ray:
Yeah. When I was driving to work one day…and my hands are just shaking like this…
But yeah, it’s just weird, you know, having your hands move, no explanation…
Rhonda:
At that time, I was feeling a little bit desperate, like, something needs to change. We can’t do this anymore.
Onscreen text:
When Ray fell out of bed and dislocated his shoulder, Rhonda realized it was time to talk to Ray’s doctor.
Rhonda:
We made an appointment with the neurologist that week talking to her about how bad it had gotten.
And she said, well, I have this drug that I would like for you to try.
Onscreen text:
Ray’s doctor started him on AUSTEDO, and as his dose was titrated, Ray and Rhonda began noticing an improvement in Ray’s chorea.
More than 3 years later, Ray is still taking AUSTEDO at 48 mg/day. His chorea movements have remained minimal.
Disclaimer at bottom of screen:
Once-daily AUSTEDO XR is available.
Bioequivalence of once-daily AUSTEDO XR has been established with AUSTEDO BID based on pharmacokinetic profile studies.
When two formulations are shown to be bioequivalent, they are considered to be therapeutically equivalent.
Rhonda:
Yeah. So his movements just became less and less as…the doses increased…
His sleeping now is very different…no more kicks, no more punches, no more flailing around in bed.
And…we both noticed that the small things that he would do with his hands became easier.
Ray:
Yeah.
Rhonda:
Buttoning his shirt, putting the leash on the dog’s collar, tying shoes. Those things became easier.
So yeah…it has far exceeded our expectations…
Onscreen text:
Today, Ray and Rhonda are still on the move—enjoying an active lifestyle and making the most of each day together.
Rhonda:
We’re looking forward to taking a trip to Yellowstone, hopefully taking our grandkids and doing some hiking…
I don’t know that we would have been able to continue hiking with his chorea had it continued on without the medication…
I feel like that we’re actually like living the way we’ve always wanted to live now…
…by going on vacations and being outdoors a lot more and having grandkids…
And yeah, I can’t image life if he didn’t have the medication.
Ray:
It really is a deal-maker for me. It just helped so much.
Onscreen text:
WHAT COULD LONG-TERM RESULTS MEAN FOR YOUR PATIENTS WITH HD CHOREA?
Learn more at AUSTEDOhcp.com
Onscreen ISI scroll:
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are indicated in adults for the treatment of chorea associated with Huntington’s disease and for the treatment of tardive dyskinesia.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Depression and Suicidality in Patients with Huntington’s Disease:
AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO can increase the risk of depression and suicidal thoughts and behavior (suicidality) in patients with Huntington’s disease. Balance the risks of depression and suicidality with the clinical need for treatment of chorea. Closely monitor patients for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidality, or unusual changes in behavior. Inform patients, their caregivers, and families of the risk of depression and suicidality and instruct them to report behaviors of concern promptly to the treating physician. Exercise caution when treating patients with a history of depression or prior suicide attempts or ideation. AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are contraindicated in patients who are suicidal, and in patients with untreated or inadequately treated depression.
Contraindications: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are contraindicated in patients with Huntington’s disease who are suicidal, or have untreated or inadequately treated depression. AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are also contraindicated in: patients with hepatic impairment; patients taking reserpine or within 20 days of discontinuing reserpine; patients taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), or within 14 days of discontinuing MAOI therapy; and patients taking tetrabenazine or valbenazine.
Clinical Worsening and Adverse Events in Patients with Huntington’s Disease: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may cause a worsening in mood, cognition, rigidity, and functional capacity. Prescribers should periodically re-evaluate the need for AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO in their patients by assessing the effect on chorea and possible adverse effects.
QTc Prolongation: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may prolong the QT interval, but the degree of QT prolongation is not clinically significant when AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO is administered within the recommended dosage range. AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO should be avoided in patients with congenital long QT syndrome and in patients with a history of cardiac arrhythmias.
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS), a potentially fatal symptom complex reported in association with drugs that reduce dopaminergic transmission, has been observed in patients receiving tetrabenazine. The risk may be increased by concomitant use of dopamine antagonists or antipsychotics. The management of NMS should include immediate discontinuation of AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO; intensive symptomatic treatment and medical monitoring; and treatment of any concomitant serious medical problems.
Akathisia, Agitation, and Restlessness: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may increase the risk of akathisia, agitation, and restlessness. The risk of akathisia may be increased by concomitant use of dopamine antagonists or antipsychotics. If a patient develops akathisia, the AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO dose should be reduced; some patients may require discontinuation of therapy.
Parkinsonism: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may cause parkinsonism in patients with Huntington’s disease or tardive dyskinesia. Parkinsonism has also been observed with other VMAT2 inhibitors. The risk of parkinsonism may be increased by concomitant use of dopamine antagonists or antipsychotics. If a patient develops parkinsonism, the AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO dose should be reduced; some patients may require discontinuation of therapy.
Sedation and Somnolence: Sedation is a common dose-limiting adverse reaction of AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO. Patients should not perform activities requiring mental alertness, such as operating a motor vehicle or hazardous machinery, until they are on a maintenance dose of AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO and know how the drug affects them. Concomitant use of alcohol or other sedating drugs may have additive effects and worsen sedation and somnolence.
Hyperprolactinemia: Tetrabenazine elevates serum prolactin concentrations in humans. If there is a clinical suspicion of symptomatic hyperprolactinemia, appropriate laboratory testing should be done and consideration should be given to discontinuation of AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO. Binding to Melanin-Containing Tissues: Deutetrabenazine or its metabolites bind to melanin-containing tissues and could accumulate in these tissues over time. Prescribers should be aware of the possibility of long-term ophthalmologic effects.
Common Adverse Reactions: The most common adverse reactions for AUSTEDO (>8% and greater than placebo) in a controlled clinical study in patients with Huntington’s disease were somnolence, diarrhea, dry mouth, and fatigue. The most common adverse reactions for AUSTEDO (4% and greater than placebo) in controlled clinical studies in patients with tardive dyskinesia were nasopharyngitis and insomnia. Adverse reactions with AUSTEDO XR extended-release tablets are expected to be similar to AUSTEDO tablets.
Please see full Prescribing Information, including Boxed Warning, on AUSTEDOhcp.com.
Onscreen text:
This was an individual patient’s experience. Results may vary.
Reference: Data on file. Parsippany, NJ: Teva Neuroscience, Inc.
Watch: ARC-HD Trial Results
Dr. Fahd Amjad discusses long-term results through 3 years.
For more videos, visit the YouTube page.
Voiceover/Onscreen text:
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
AUSTEDO® XR (deutetrabenazine) extended-release tablets and AUSTEDO® (deutetrabenazine) tablets are indicated in adults for the treatment of chorea associated with Huntington’s disease and for the treatment of tardive dyskinesia.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Depression and Suicidality in Patients with Huntington’s Disease: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO can increase the risk of depression and suicidal thoughts and behavior (suicidality) in patients with Huntington’s disease. Balance the risks of depression and suicidality with the clinical need for treatment of chorea. Closely monitor patients for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidality, or unusual changes in behavior. Inform patients, their caregivers, and families of the risk of depression and suicidality and instruct them to report behaviors of concern promptly to the treating physician. Exercise caution when treating patients with a history of depression or prior suicide attempts or ideation. AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are contraindicated in patients who are suicidal, and in patients with untreated or inadequately treated depression.
Please see additional Important Safety Information at the end of this video.
Fahd Amjad:
Hello. I am Dr. Fahd Amjad, Co-Director of the Huntington’s Disease Care, Education, Research Center at Georgetown University Medical Center in Washington, DC.
For over 10 years, I have led our mission to provide treatment to and manage the symptoms experienced by patients with Huntington’s disease, or HD.
I ran into a colleague the other day, and thought I would share the conversation we had about our patients with HD chorea. More than 90 percent of patients with HD have chorea, and as neurologists, we appreciate the challenges faced by patients with chorea symptoms.
We both regularly observe that patients with chorea have difficulty walking and may fall. My colleague recently started managing a new patient with chorea symptoms and wanted to understand what my goals are for patients. Because patients with chorea are at risk of falls, they often become dependent on their partners or caregivers for help with their daily activities. One of my goals is to help patients maintain their independence for as long as possible.
I asked my colleague what he prescribes for his patients with chorea. Both of us consider AUSTEDO, a vesicular monoamine transporter 2 inhibitor, or VMAT2, for the management of chorea symptoms in patients with HD.
I choose AUSTEDO because its efficacy and safety were demonstrated in a randomized, 12-week, placebo-controlled study in patients with chorea associated with HD. The results showed a statistically significant reduction in chorea of the face, mouth, trunk, arms, and legs as measured by the total maximal chorea score.
AUSTEDO is also the first VMAT2 inhibitor to have physicians and patients rate overall HD chorea symptoms as “much improved” or “very much improved” when compared to placebo as measured by the Clinical Global Impression of Change and Patient Global Impressions of Change scales.
I mentioned to him that I recently reviewed a 3-year open-label extension study called ARC-HD, published in CNS Drugs. This AUSTEDO study interests me as a provider because HD is a progressive condition, and the study demonstrated about 3 years of continued control of chorea in patients.
Disclaimer at bottom of page:
Patients who participated in the clinical trials discussed in this testimonial received the BID formulation for AUSTEDO.
Fahd Amjad:
I am also confident in the demonstrated safety profile of AUSTEDO and explain to my patients that the most common side effects include somnolence, diarrhea, dry mouth, and fatigue. These side effects occur most often during the dosing titration phase.
Most of my patients are on an average daily of 36 mg with some up to 48 mg, which aligns with the clinical trials for AUSTEDO. And I can also offer my patients more options with the introduction of AUSTEDO XR, a once-daily formulation.
Voiceover/Onscreen text:
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
AUSTEDO® XR (deutetrabenazine) extended-release tablets and AUSTEDO® (deutetrabenazine) tablets are indicated in adults for the treatment of chorea associated with Huntington’s disease and for the treatment of tardive dyskinesia.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Depression and Suicidality in Patients with Huntington’s Disease: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO can increase the risk of depression and suicidal thoughts and behavior (suicidality) in patients with Huntington’s disease. Balance the risks of depression and suicidality with the clinical need for treatment of chorea. Closely monitor patients for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidality, or unusual changes in behavior. Inform patients, their caregivers, and families of the risk of depression and suicidality and instruct them to report behaviors of concern promptly to the treating physician. Exercise caution when treating patients with a history of depression or prior suicide attempts or ideation. AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are contraindicated in patients who are suicidal, and in patients with untreated or inadequately treated depression.
Contraindications: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are contraindicated in patients with Huntington’s disease who are suicidal, or have untreated or inadequately treated depression. AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are also contraindicated in: patients with hepatic impairment; patients taking reserpine or within 20 days of discontinuing reserpine; patients taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), or within 14 days of discontinuing MAOI therapy; and patients taking tetrabenazine or valbenazine.
Clinical Worsening and Adverse Events in Patients with Huntington’s Disease: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may cause a worsening in mood, cognition, rigidity, and functional capacity. Prescribers should periodically re-evaluate the need for AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO in their patients by assessing the effect on chorea and possible adverse effects.
QTc Prolongation: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may prolong the QT interval, but the degree of QT prolongation is not clinically significant when AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO is administered within the recommended dosage range. AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO should be avoided in patients with congenital long QT syndrome and in patients with a history of cardiac arrhythmias.
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS), a potentially fatal symptom complex reported in association with drugs that reduce dopaminergic transmission, has been observed in patients receiving tetrabenazine. The risk may be increased by concomitant use of dopamine antagonists or antipsychotics, The management of NMS should include immediate discontinuation of AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO; intensive symptomatic treatment and medical monitoring; and treatment of any concomitant serious medical problems.
Akathisia, Agitation, and Restlessness: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may increase the risk of akathisia, agitation, and restlessness. The risk of akathisia may be increased by concomitant use of dopamine antagonists or antipsychotics. If a patient develops akathisia, the AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO dose should be reduced; some patients may require discontinuation of therapy.
Parkinsonism: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may cause parkinsonism in patients with Huntington’s disease or tardive dyskinesia. Parkinsonism has also been observed with other VMAT2 inhibitors. The risk of parkinsonism may be increased by concomitant use of dopamine antagonists or antipsychotics. If a patient develops parkinsonism, the AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO dose should be reduced; some patients may require discontinuation of therapy.
Sedation and Somnolence: Sedation is a common dose-limiting adverse reaction of AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO. Patients should not perform activities requiring mental alertness, such as operating a motor vehicle or hazardous machinery, until they are on a maintenance dose of AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO and know how the drug affects them. Concomitant use of alcohol or other sedating drugs may have additive effects and worsen sedation and somnolence.
Hyperprolactinemia: Tetrabenazine elevates serum prolactin concentrations in humans. If there is a clinical suspicion of symptomatic hyperprolactinemia, appropriate laboratory testing should be done and consideration should be given to discontinuation of AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO.
Binding to Melanin-Containing Tissues: Deutetrabenazine or its metabolites bind to melanin-containing tissues and could accumulate in these tissues over time. Prescribers should be aware of the possibility of long-term ophthalmologic effects.
Common Adverse Reactions: The most common adverse reactions for AUSTEDO (>8% and greater than placebo) in a controlled clinical study in patients with Huntington’s disease were somnolence, diarrhea, dry mouth, and fatigue. The most common adverse reactions for AUSTEDO (4% and greater than placebo) in controlled clinical studies in patients with tardive dyskinesia were nasopharyngitis and insomnia. Adverse reactions with AUSTEDO XR extended-release tablets are expected to be similar to AUSTEDO tablets.
Please see full Prescribing Information, including Boxed Warning, at AUSTEDOhcp.com.
For more videos, visit the YouTube page.
HD, Huntington’s disease; TMC, total maximal chorea; VMAT2, vesicular monoamine transporter 2.
REFERENCES: 1. Frank S, Testa C, Edmondson MC, et al. The safety of deutetrabenazine for chorea in Huntington disease: an open-label extension study. CNS Drugs. 2022;36(11):1207-1216. 2. Xenazine® (tetrabenazine) tablets. Prescribing Information. Deerfield, IL: Lundbeck Inc. 3. Stimming EF, Claassen DO, Kayson E, et al; Huntington Study Group KINECT-HD Collaborators. Safety and efficacy of valbenazine for the treatment of chorea associated with Huntington’s disease (KINECT-HD): a phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2023;22(6):494-504. 4. Data on file. Parsippany, NJ: Teva Neuroscience, Inc. 5. AUSTEDO XR® (deutetrabenazine) extended-release tablets and AUSTEDO® current Prescribing Information. Parsippany, NJ: Teva Neuroscience, Inc.
